What you need to know about Cauda Equina Syndrome Treatment
Contents
- 1 What you need to know about Cauda Equina Syndrome Treatment
- 2 What does the Procedure Involve?
- 3 How Long Should I Stay in the Area?
- 4 What’s the Recovery Time?
- 5 What About Aftercare?
- 6 What’s the Success Rate?
- 7 Are there Alternatives to CES Treatment?
- 8 What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a rare condition that occurs when the spinal nerve roots are compressed, disturbing motor, and sensory function to the lower extremities and bladder. CES usually is a surgical emergency because it can lead to incontinence and possibly permanent paralysis of the legs. Once you are diagnosed with the condition, surgery must be performed quickly to prevent permanent damage and will need to be done within 24 or 48 hours.
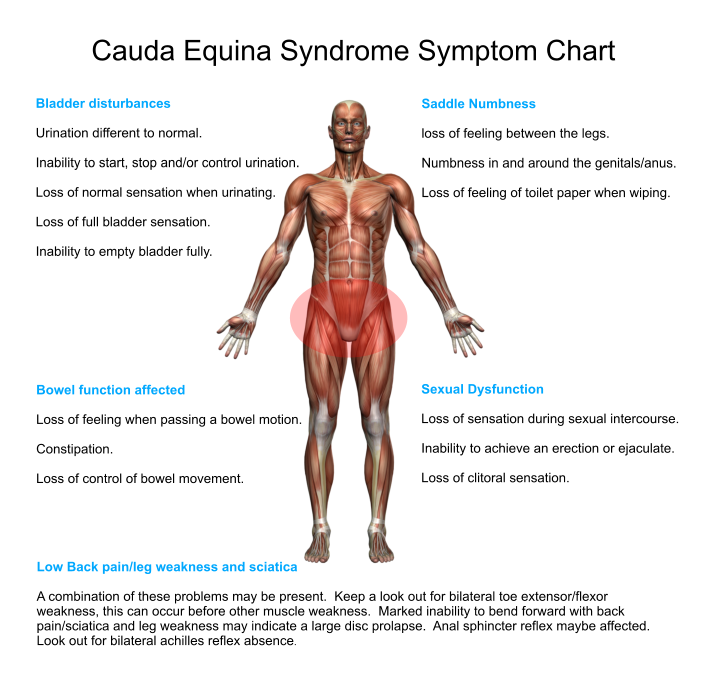
What does the Procedure Involve?
Urgent spinal decompression surgery is usually the treatment of choice for cauda equina syndrome. The most common form of surgery is called a lumbar laminectomy, which can be used to move a herniated disc back into its original position. A similar procedure, called a discectomy, may be performed to remove disc material or pieces of bone pressing on the cauda equina.
During spinal decompression surgeries, you will be given general anesthesia. Your surgeon will start the procedure by making an incision in the lower back at the site of the pressure. Then, the muscles, tissues, and protective lamina that surrounds the nerves will be moved aside to access the source of pressure. Your surgeon will then repair a herniated disc, remove a tumor, or repair a lesion to relieve the pressure. Once the procedure is complete, the incision will be closed with stitches.
Treatment for CES does not end with surgery. In most cases, you will need further treatment. The treatment options include:
-
Medication is normally used for long-term treatment. The medication prescribed may include corticosteroids to reduce swellings, pain medication (such as ibuprofen) for pain management, and antibiotics if your CES is caused by an infection. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medication for better bladder and bowel control, such as oxybutynin, tolterodine, and hyoscyamine.
-
Radiotherapy or chemotherapy may be required after surgery if a tumor is responsible for your CES.
-
Physical therapy is usually included as part of your treatment plan if CES impacted your ability to walk. A physical therapist can give you exercises to help improve your stride and help you regain your strength. If everyday activities, such as getting dressed, are affected by CES, an occupational therapist can also help you.
How Long Should I Stay in the Area?
After surgery, you may need to stay in the hospital for four to five days. You should be able to leave the area within 10 to 14 days if no further treatment is needed or if you choose to have it back at home. However, if you decided to undergo your whole treatment plan (radiotherapy or chemotherapy and physical therapy) in the country, you may need to stay a lot longer, depending on the schedule of your treatment. Make sure to talk to your medical team regarding this matter.
What’s the Recovery Time?
Recovery time after CES treatment can take a long time. Recover from the decompression surgery can take about four to six weeks. If your job does not require any physical activities, you may be able to return in four weeks. However, if your job is physically demanding, you may need four months before you can return to work.
It is important to remember that healing from the surgery itself is just one part of recovering from CES. For some people, it may take many months or even several years to fully recover.
What About Aftercare?
During your recovery period, you will need to see your doctor periodically so they can check your progress. Your doctor will give you post-operative instructions that you will need to follow.
If you experience loss of bladder and bowel function, you may need to use a catheter to completely empty your bladder around three to four times a day. To prevent infection, drink plenty of fluids, and ensure good personal hygiene. To prevent leaks, you can wear protective pads and pants.
Emotional or psychological counseling may help you adjust to living with CES. The support of your family and friends is also important during your recovery. Therefore, talk to them and include them to help them understand what you are dealing with.
What’s the Success Rate?
The success rate of CES treatment depends on several factors, such as the degree of nerve damage at the time of surgery and how quickly the nerve is decompressed. Full recovery is possible, but some people may experience some lingering symptoms.
CES treatment is generally safe and effective, but there are some risks to be aware of. These include recurrent or continuing symptoms, infection, blood clots, dural tear, and leakage of cerebrospinal fluid, nerve injury, and paralysis.
Are there Alternatives to CES Treatment?
Since cauda equine syndrome is a medical emergency, there is no alternative to surgical decompression. If the condition is left untreated, you could develop permanent incontinence and become paralyzed.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before treatment, you may experience serious lower back pain, loss of reflexes in your lower extremities, and other symptoms that interfere with your daily life. The condition may also be dangerous and cause permanent damage. After successful and timely treatment, the symptoms should be gone and you may be able to recover completely.
For an in-depth analysis of a Cauda Equine Syndrome Treatment, watch this short video.
To check prices or to book a Cauda Equine Syndrome Treatment, in Thailand or anywhere else in the world, head on over to MyMediTravel now!