People who want to address different visual problems without using eyeglasses are increasingly choosing contact lenses. Usually composed of silicone or plastic, these are tiny discs that are intended to sit directly on the surface of the eye. Providing you with a wide field of vision and almost flawless vision correction, today’s market is filled with some varieties, each with unique advantages and disadvantages based on the needs and general health of the user’s eyes.
These contact lenses have revolutionized the field of optometry by providing an alternative to eyeglasses. From that point on, they have diversified over the years and are made from a variety of materials for contact lenses. Contact lenses are also available for a variety of vision and aesthetic solutions whether as an alternative for glasses in various powers or as a form of expression with coloured lenses.
The History of Contact Lenses
Contents
The notion of contact lenses was first conceived in the sixteenth century by the Italian scientist Leonardo da Vinci. However, the first eye covering that could be seen through and tolerated wasn’t created until the late 19th century by German glassblower F.E. Muller. Adolf Fick, a Swiss physician, created the first contact lens in 1887 to treat vision problems.

As science and technology progressed, so did the contact lens materials used to manufacture these vision-enhancing devices. Initially made from glass, they were uncomfortable and could only be worn for a few short hours. Later, Plexiglas lenses emerged, which then led to the creation of the modern soft contact lens in the 1970s – made from a hydrophilic or “water-loving” plastic also known as a soft polymer.
The Different Types of Contact Lenses
There are various contact lens types available in the market today. Major categories include soft contact lenses, hard or Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) contact lenses, and hybrid contact lenses.
Type: Soft
The most common kind of contact lenses in the world are soft contact lenses. Since they are composed of pliable, supple polymers, oxygen can get through to the cornea. They come in many variants, such as everyday wear (to be discarded before bed) and extended wear (to be worn overnight), and are renowned for their instant comfort.
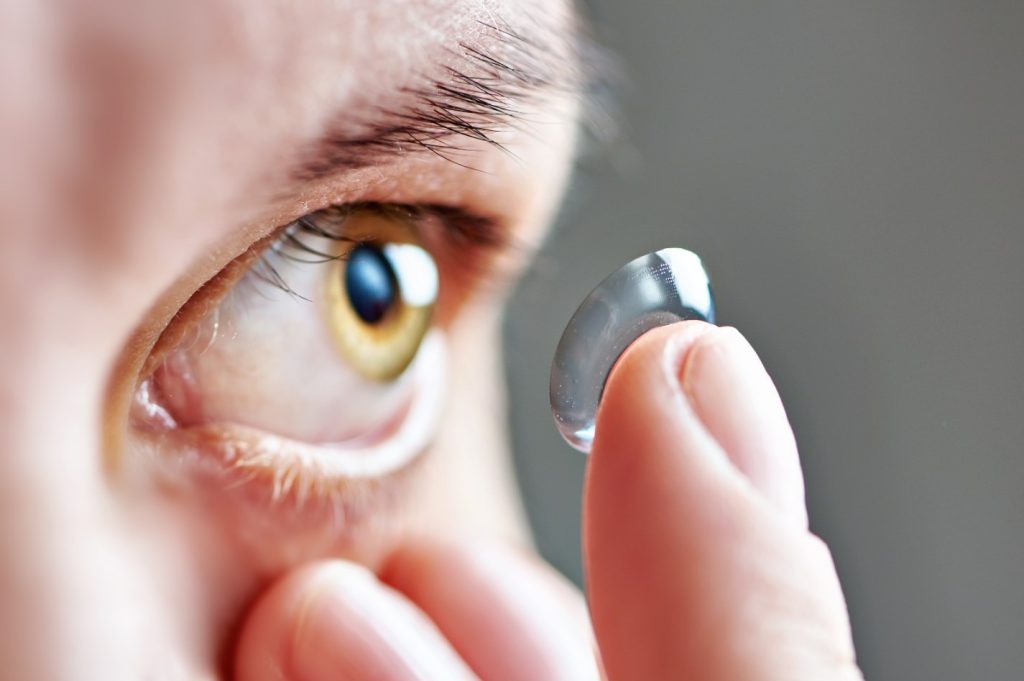

The main advantages of soft lenses are their comfort and the fact that they come in a variety of forms that can virtually cure any visual issue. Compared to hard/RGP lenses, they are more likely to cause an eye infection and need more frequent cleaning and maintenance.
Type: Hard/RGP
Hard or Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) contact lenses are usually composed of sturdy and durable plastics that transmit oxygen. Unlike soft lenses, Hard/RGP lenses maintain their shape while in use and offer clearer vision, longer lifespan, and greater resistance to deposit buildup.
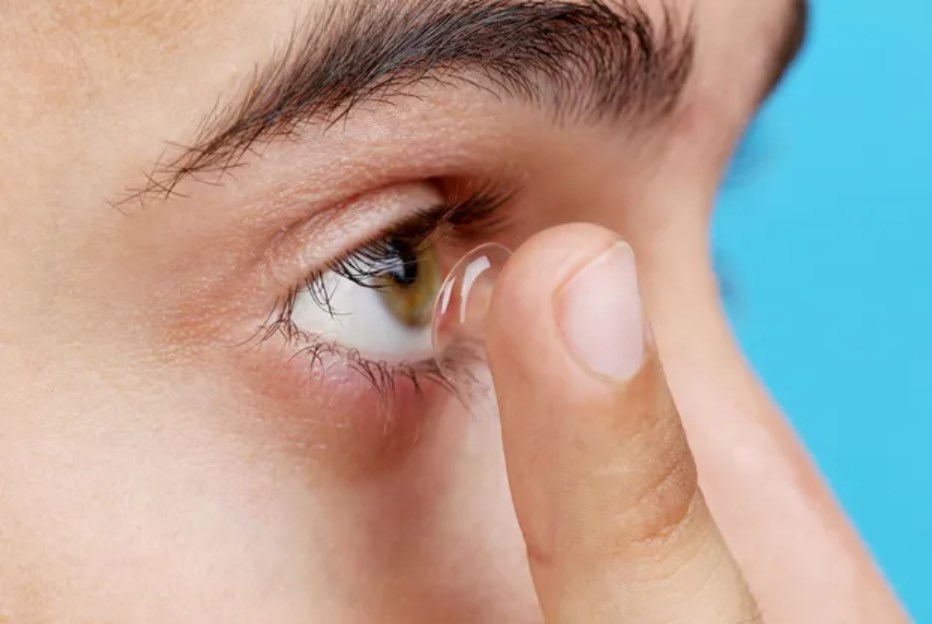

While these upsides are nice, there are downsides to using these contact lenses they require a longer adjustment period and are more likely to be dislodged from the eye in comparison to soft contact lenses.
Whether you use the soft contact lens or the hard ones, these depend on the factors in your life such as your vision correction needs, lifestyle, and personal preference.
Materials Used
How to Choose the Best Option for you
Choosing the best contact lenses for you involves considering a few key factors. First, the type of vision problem you are having such as myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, or presbyopia will determine which contact lens type would be the best for you. On top of these, your lifestyle will play a role as well and if you are involved in a lot of physical activity, you might prefer soft lenses that will stay in place better for these occasions.
As exciting as it is to forego eyeglasses, you cannot ignore your eye health where certain conditions like dry eyes or allergies. In these cases, you are better off with daily disposable lenses. Finally, it is important to always consult with an optometrist before you make a decision, they will provide you with comprehensive advice based on a thorough eye examination that will allow you to make the best decisions for your eye medical journey.

