What you need to know about Stent Insertion
Contents
- 1 What you need to know about Stent Insertion
- 2 What does the Procedure Involve?
- 3 How Long Should I Stay in at my Destination?
- 4 What’s the Recovery Time?
- 5 What About Aftercare?
- 6 What’s the Success Rate?
- 7 Are there Alternatives to Stent Insertion?
- 8 What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
A stent is a tiny wire mesh stainless steel tube used to keep a blocked artery open and prevent it from closing again. Depending on where it is placed, it can restore the flow of blood or other fluids. Stents usually become a permanent part of your artery, but some stents are temporary.
You may need a stent when a blood vessel is blocked by fatty deposits or plaque. Plaque is made of various substances, such as cholesterol, that attach to the walls of a vessel. A stent may also be required during an emergency procedure, which is more common if a coronary artery (an artery of the heart) is blocked. Stents can also be used to prevent aneurysms in your brain, aorta, or other blood vessels from rupturing.
While stents are most commonly used to keep blood vessels open, it can actually open other passageways as well, including:
-
Ureters – these are the tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
-
Bronchi – these are the small airways in the lungs.
-
Bile ducts – these are the tubes that transport bile to and from digestive organs.
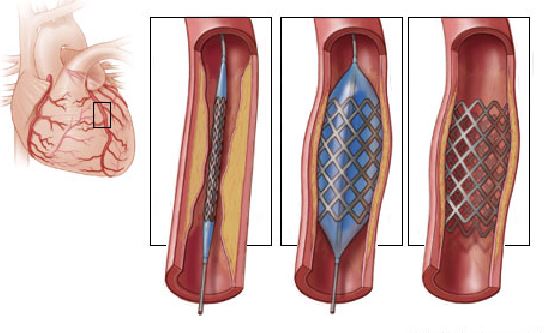
What does the Procedure Involve?
Stent insertion is often performed using a minimally invasive procedure. Your doctor will make a small incision, usually in your arm or groin, to insert a tiny, flexible tube called a catheter. The catheter is used to guide specialized tools through your blood vessels to reach the site of the blockage. One of the tools may have a camera attached on its end to help your doctor guide the stent.
During the procedure, an angiogram may be used to help your doctor guide the stent through the vessel. An angiogram is an imaging technique in which a special dye (contrast) is injected through the catheter to make the arteries visible on the TV monitors.
Once the broken or blocked vessel is located and the necessary tools reach the area that needs a stent, your doctor will install the stent and leave it in place permanently. Then, the tools are removed from your body and the incision is closed.
You will be given local anesthesia during the procedure. This means that you will be awake, but the affected area will be numbed. Your doctor may also give you a sedative to help you relax.
How Long Should I Stay in at my Destination?
You may need to stay in the hospital overnight after stent insertion. However, if the stent insertion is needed because of an emergency, such as a stroke or heart attack, you will need to stay in the hospital longer. The recommended length of stay will be around 7 days since you need to let your body recover before traveling and you will need to attend a follow-up checkup.
What’s the Recovery Time?
Most people are able to return to work and most normal activities within 5-7 days following successful stent insertion surgery. However, strenuous activities, such as vigorous exercise and heavy lifting, should be avoided for several weeks.
What About Aftercare?
During your recovery period, your doctor will prescribe antiplatelet drugs, which can help prevent blood clots from forming near the stent. You may need to take the antiplatelet drug daily for an indefinite period of time after stent insertion.
Healthy lifestyle changes are vital after stent insertion to prevent plaque building up in the body and to prevent further complications. It is recommended that you:
-
Exercise regularly
-
Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet
-
Maintain a healthy weight
-
Quit smoking
-
Reduce stress.
You may need to attend regular follow-up appointments, usually every six months for the first year of your stent insertion. During these appointments, your doctor will evaluate your medications, monitor your progress, determine how the stent is working for you, and check the status of your disease. You can choose to have follow-up appointments in your home country.
What’s the Success Rate?
Stent insertion is a generally safe procedure with a high success rate. It is one of the most effective methods to keep a blocked passageway open.
Although it is very safe, you need to remember that any surgical procedure has risks. For stent insertion, the risks include breathing problems, infection, bleeding, blood clots, heart attack, and the re-narrowing of the artery.
In some very rare cases, stent insertion may also cause strokes and seizures. There is also a very slight chance that your body will reject the stent.
Are there Alternatives to Stent Insertion?
Depending on your specific condition, doctors may sometimes offer medication as an alternative to a stent. For plaques or fatty deposits in the blood vessels, your doctor may offer a procedure to remove the fatty deposits (percutaneous transluminal coronary rotational atherectomy – PTCRA) or a procedure to burn the fatty deposits (percutaneous laser coronary angioplasty). For some patients, coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) is also an alternative option.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before the procedure, you may have a blockage in a passageway in your body, such as your artery, ureters, and bile ducts. The blockage can be dangerous and cause painful symptoms. After successful stent insertion, the symptoms should be reduced. You can go back to living a full and active life after your stent insertion.
For an in-depth analysis of a Stent Insertion Procedure, watch this short video.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=CQMEZuU1EvE
To check prices or to book a Stent Insertion Procedure, in Thailand or anywhere else in the world, head on over to MyMediTravel now!

