Egg Freezing, also known as Oocyte Cryopreservation, is a way of preserving a patient’s fertility so she can try to have a family in the future. It involves collecting eggs, freezing them and then thawing them later on so they can be used for fertility treatment.
Some patients freeze their eggs because they have a medical condition or are undergoing treatment that affects their fertility. It can also be used by women who aren’t ready or able to have children and want the chance of conceiving in the future. When you go for your initial consultation and evaluation with the specialist, ask questions regarding success rates and the risks involved.
You will need to be tested for any infectious diseases like HIV and Hepatitis. This has no bearing on whether you can freeze your eggs, it is to ensure that affected egg samples are stored separately to prevent contamination of other samples.
You’ll then start the IVF (In vitro fertilization) process, which usually takes around two to three weeks to complete. Normally this will involve taking drugs to boost your egg production and help the eggs mature. When they’re ready, they’ll be collected whilst you’re under general anesthetic or sedation using an ultrasound-guided probe. The needle attached will pass through the vaginal wall and into the ovary, where it will draw the eggs. This can take less than 20 minutes and you can there is no need for overnight stay.
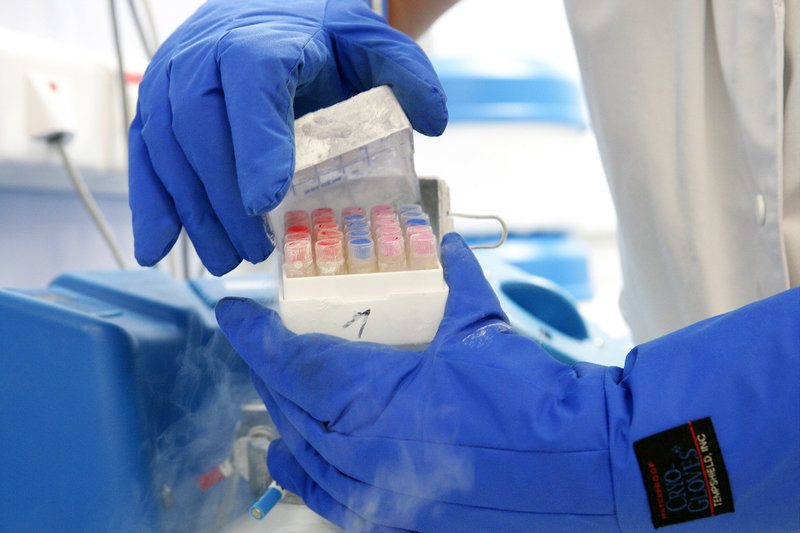
At this point, instead of mixing the eggs with sperm (as in conventional IVF) a cryoprotectant (freezing solution) will be added to protect the eggs. The eggs will then be frozen either by cooling them slowly or by vitrification (fast freezing) and stored in tanks of liquid nitrogen.
Most patients will have around 15 eggs collected although this isn’t always possible for those with low ovarian reserves (low numbers of eggs). When you want to use them, the eggs will be thawed and must be fertilized using a fertility treatment called ICSI, as the freezing process makes the outer coating around the eggs tougher and sperm may be unable to penetrate it naturally under IVF.
You’ll need to complete consent forms before you start treatment specifying how you want your eggs to be used. This includes information on how long you want the eggs to be stored for (the standard period is 5 – 10 years), what should happen to your eggs if you were to die or become unable to make decisions for yourself, whether the eggs are to be used for your own treatment only, or whether they can be donated for someone else’s treatment, or used for research or training if you don’t want to use them or any other conditions you may have for the use of your eggs.
Whilst egg freezing is a great option if you’re approaching 40 and not yet ready to have a child/children but you’re keen to in the future, it is also considered the solution to some medical conditions or circumstances that may affect your fertility, such as:
- Ovarian disease with risks that may damage your ovaries.
- A genetic mutation that may require removing your ovaries.
- Surgery that may damage your ovaries.
- If you have cancer that requires chemotherapy and/or pelvic radiation therapy (these may affect your fertility).
- Chromosomal abnormalities – poses risks of premature ovarian failure.
Unlike fertilized egg freezing or embryo cryopreservation, this form of the procedure will not require sperm because your eggs will not be fertilized before being frozen.
If you are considering freezing your eggs, note that the medical professionals you’ll be dealing with are Reproductive Endocrinologists. Generally, you will be able to acquire the healthiest eggs before you reach 30, the younger you are, the better, simply because at a younger age you will be able to produce and freeze more eggs in one cycle.
The Procedure
Contents
Before you begin your egg freezing process, you need to first undergo a series of blood tests as an assessment, these include:
- Infectious disease screening – this will determine if you have an infectious disease like HIV or Hepatitis to ensure that your affected eggs will be stored separately to prevent them from contaminating the other eggs.
- Ovarian reserve testing – this will determine the quality and quantity of your eggs. The results may also help predict how your ovaries will respond to fertility medications.
You also have to expect that Egg Freezing follows a series of steps; furthermore, egg retrieval will closely follow a similar process to IVF:
Ovarian stimulation – during this first step, you will be given hormonal injection one to several weeks to produce multiple eggs. Your doctor may also give you medications to prevent premature ovulation.
Egg retrieval – this will be done under sedation. Typically, an ultrasound probe will be inserted into your vagina to determine the follicle, a needle will then be guided through your vagina and into the follicle. A suction connected to the needle will be the one to retrieve the eggs from the follicle.
Freezing – after your eggs are harvested, they will now be cooled to a subzero temperature to preserve them for future use.
Although the procedure will differ from country to country and even the hospitals/clinics in an area may differ somewhat, but in general, you can expect the following steps carried out over two separate trips:
- Consultation & evaluation with the specialist. Such evaluations may include a physical examination, blood screening (including Thalassemia and serology testing), pelvic examination, cervical cancer screening, and transvaginal ultrasound.
- If everything is clear after the initial consultation & evaluation with the specialist, you will need to come back to Hospital/Clinic on the second day of your menstrual for a hormone test (FSH & Estrogen).
- You will be prescribed with a medication to be injected daily for 10 days (starting on the second day of the menstrual cycle until the twelfth day of cycle).
- An Ovum pick-up procedure will be performed on the twelfth day of the cycle (this is performed without the need to be present).
- Egg Freezing performed and eggs will be frozen for a pre-determined number of years with the option to unfreeze them at any time.
Length of Stay in Destination
Usually, you can go home immediately after your procedure. Egg retrieval takes roughly about 20 minutes to finish and you will not need any stitches after the procedure since your doctor will not perform any cutting. Just bear in mind that you’ll need to plan two separate trips, with the second being timed around your menstrual cycle.
Recovery Time
You can typically go back to your normal activities, including work and exercise within a week of your egg retrieval. Your doctor will also advise you to avoid having unprotected sex to prevent you from having an unintended pregnancy.
Aftercare
The whole process of egg freezing may take between 10 to 14 days. You may freeze your eggs in the long term even for about 10 years. Long term aftercare will not be required.
Success Rate
Given the time when you are ready to have a child, your frozen eggs will be thawed, fertilized with a sperm in a lab and then implanted into your uterus or your gestational carrier’s uterus (if in case).
Your chances of getting pregnant after implantation will depend on your age and the time of freezing. It is also important to know that the older you are at the time of your egg freezing, the lower the chances that you’ll achieve childbirth. In addition, your chances of becoming pregnant after implantation are usually about 30% to 60%.
Another important thing to know is that Egg freezing also carries out several risks, these risks include:
- Egg retrieval procedure – although a rare occurrence, the use of an aspirating needle to harvest eggs may cause bleeding, infection or damage to your bowel, bladder or blood vessel.
- Emotional risks – although this will give you hope for future pregnancy, achieving success is no guarantee.
- Conditions associated with the use of fertility drugs – fertility drug injectable may cause your ovaries to be swollen and become painful after ovulation or egg retrieval.
Alternatives to Egg freezing Procedures
Ovarian Tissue freezing or Ovarian Tissue Banking is one alternative to egg freezing. This is one method of fertility wherein the outer layer of your ovary, which contains a large number of immature eggs, will be taken out of your body and also be frozen for future use.
Another alternative is embryo freezing, typically after IVF treatment, your ovaries are stimulated to produce more eggs and this will be followed by fertilization and embryo culture. There will usually be an excess of good embryos which you can freeze for future use.
For more information about Egg Freezing Procedure with before and after images, watch this short video
To check prices or to book an Egg Freezing Procedure in Thailand or anywhere else in the world, head on over to MyMediTravel now!